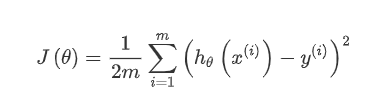1
2
3
|
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
array([[1., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 1.]])
单变量的线性回归
整个2的部分需要根据城市人口数量,预测开小吃店的利润
数据在ex1data1.txt里,第一列是城市人口数量,第二列是该城市小吃店利润。
1
2
3
|
path = 'ex1data1.txt'
data = pd.read_csv(path, header=None, names=['Population', 'Profit'])
data.head()
|
|
Population |
Profit |
| 0 |
6.1101 |
17.5920 |
| 1 |
5.5277 |
9.1302 |
| 2 |
8.5186 |
13.6620 |
| 3 |
7.0032 |
11.8540 |
| 4 |
5.8598 |
6.8233 |
1
2
|
data.plot(kind='scatter',x='Population',y='Profit', figsize=(12,8))
plt.show()
|
梯度下降
这个部分你需要在现有数据集上,训练线性回归的参数θ
1
2
3
4
|
def computeCost(X, y, theta):
inner = np.power(((X * theta.T) - y), 2)
return np.sum(inner) / (2 * len(X))
#代价函数
|
数据前面已经读取完毕,我们要为加入一列x,用于更新θ0,然后我们将θ初始化为0,学习率初始化为0.01,迭代次数为1500次
1
|
data.insert(0, 'Ones', 1)
|
1
2
3
4
|
# 初始化X和y
cols = data.shape[1]
X = data.iloc[:,:-1]#X是data里的除最后列
y = data.iloc[:,cols-1:cols]#y是data最后一列
|
|
Ones |
Population |
| 0 |
1 |
6.1101 |
| 1 |
1 |
5.5277 |
| 2 |
1 |
8.5186 |
| 3 |
1 |
7.0032 |
| 4 |
1 |
5.8598 |
|
Profit |
| 0 |
17.5920 |
| 1 |
9.1302 |
| 2 |
13.6620 |
| 3 |
11.8540 |
| 4 |
6.8233 |
代价函数是应该是numpy矩阵,所以我们需要转换X和Y,然后才能使用它们。 我们还需要初始化theta。
1
2
3
|
X = np.matrix(X.values)
y = np.matrix(y.values)
theta = np.matrix(np.array([0,0]))
|
1
2
|
X.shape, theta.shape, y.shape
#shape矩阵的维度
|
((97, 2), (1, 2), (97, 1))
计算代价函数 (theta初始值为0)
1
|
computeCost(X, y, theta)
|
32.072733877455676
梯度下降(未写)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
def gradientDescent(X, y, theta, alpha, iters):
temp = np.matrix(np.zeros(theta.shape))
parameters = int(theta.ravel().shape[1])
cost = np.zeros(iters)
for i in range(iters):
error = (X * theta.T) - y
for j in range(parameters):
term = np.multiply(error, X[:,j])
temp[0,j] = theta[0,j] - ((alpha / len(X)) * np.sum(term))
theta = temp
cost[i] = computeCost(X, y, theta)
return theta, cost
#这个部分实现了Ѳ的更新
|
1
2
|
alpha = 0.01
iters = 1500
|
1
2
|
g, cost = gradientDescent(X, y, theta, alpha, iters)
g
|
matrix([[-3.63029144, 1.16636235]])
1
2
3
4
5
|
predict1 = [1,3.5]*g.T
print("predict1:",predict1)
predict2 = [1,7]*g.T
print("predict2:",predict2)
#预测35000和70000城市规模的小吃摊利润
|
predict1: [[0.45197679]]
predict2: [[4.53424501]]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
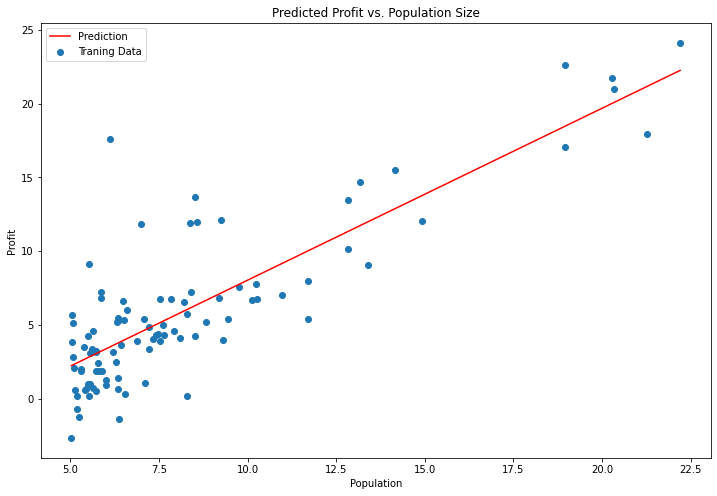
x = np.linspace(data.Population.min(), data.Population.max(), 100)
f = g[0, 0] + (g[0, 1] * x)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,8))
ax.plot(x, f, 'r', label='Prediction')
ax.scatter(data.Population, data.Profit, label='Traning Data')
ax.legend(loc=2)
ax.set_xlabel('Population')
ax.set_ylabel('Profit')
ax.set_title('Predicted Profit vs. Population Size')
plt.show()
#原始数据以及拟合的直线
|